Proton Computed Tomographic Image Reconstruction from Curved Paths
Computerized image reconstruction, specifically paths of proton particles, applicable to radiation therapy for cancer patients
Computed tomographic image reconstruction has typically focused on X-rays or photons in the body. This has become an increasingly popular way for radiation therapy for cancer treatment. Proton beams are better than X-rays and photons because they are 1) more accurate 2) leave other tissue unharmed 3) lower-cost. However, protons are heavy, thus bend when shot into the body. Therefore, imaging of the beam may not be accurate. There is a large portion of uncertainty in current uses of proton beam therapy and needs to be corrected.
This invention allows radiation specialists to target a certain area of cancer with a lower rate of uncertainty. The algorithm itself can graphically trace the positions of the cancer proton beams as they travel through the body and monitor slight movements of beams.
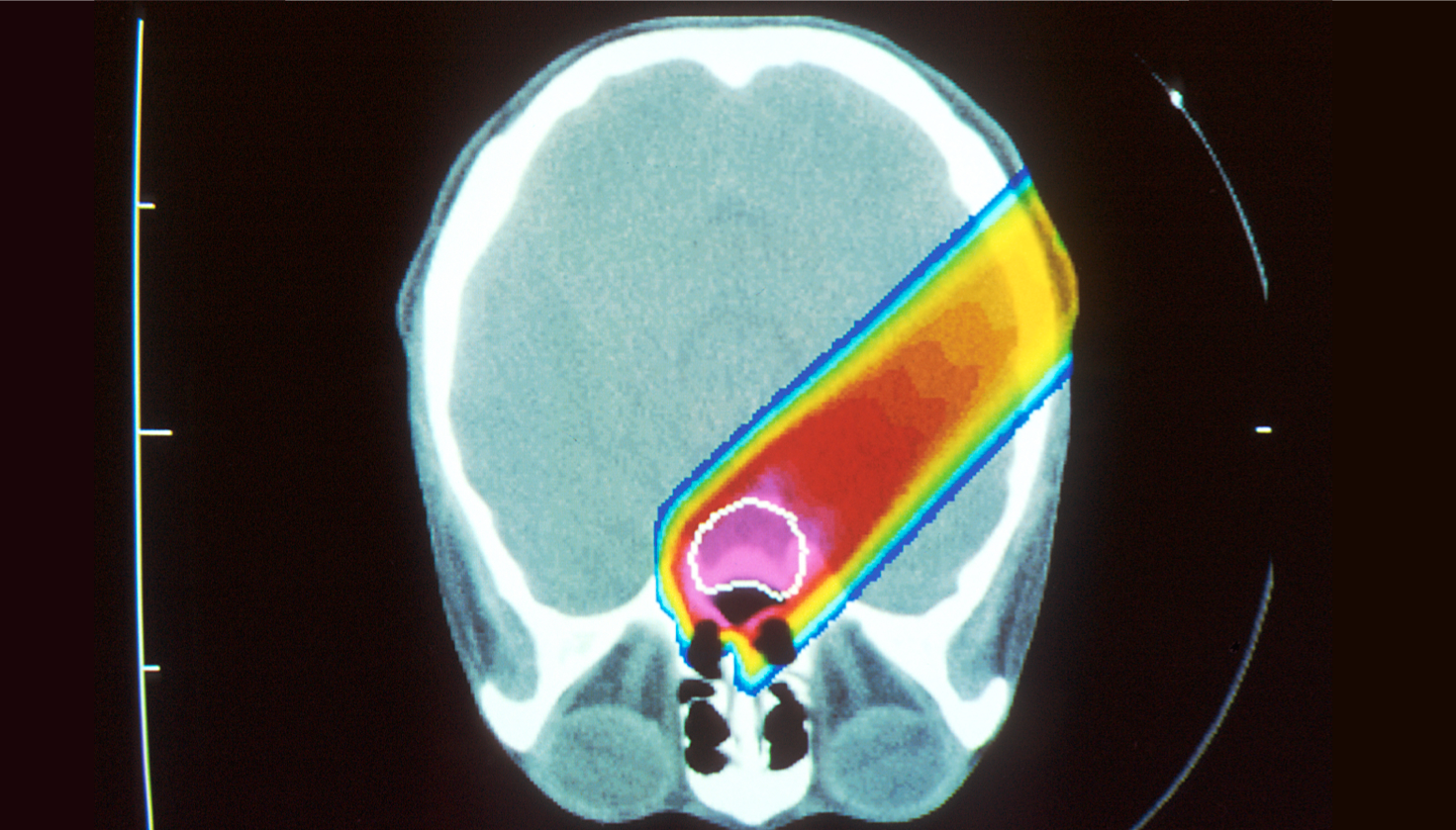 Please note, header image is purely illustrative. Source: National Cancer Institute. public domain.
Please note, header image is purely illustrative. Source: National Cancer Institute. public domain.
- Less Harmful - More Accurate - Less Expensive
- Cancer - Treatment - Biomedical Engineering - Life Sciences Clinical
Patented
9251606
Available for licensing.
Development partner,Commercial partner,Licensing
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
Patent Status |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |
|